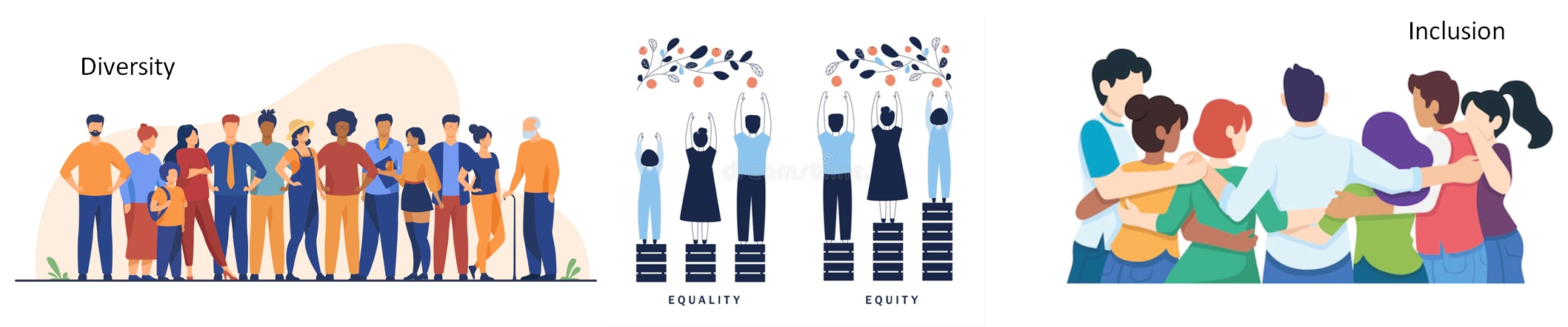
refers to existence of groups in a community, organization or workforce with heterogenous social and cultural characteristics. In any group, individuals have differences in identity aspects such as age, race, sex, gender, sexual preferences, ability/disability, ethnicity, class, caste, religion, socioeconomic status, regional and linguistic identity, et cetera. Differences also exist in access to resources and opportunities; physical and mental ability; educational preparation; employment level and job functions, et cetera. Social heterogeneity is an indicator of organizational diversity. Diversity brings together wide-ranging talent, skills and perspective. It enriches the workplace by bringing new ways of thinking, approaching and solving problems. Diverse workforce enhances creativity, effectiveness, and productivity. Increasing the participation of underrepresented groups, including women, is an area of concern and an important component of strategic vision of organizations.
is about ensuring that every individual has an equal opportunity to make the most of their lives and talents. It is also believing that no one should have poorer life chances because of the way, where and to whom they were born, where they come from, whether they have a disability, what they believe in, or because of other characteristics.
Equality recognises that historically certain groups of people with particular characteristics such as race, disability, sex and sexual orientation have and continue to experience discrimination. Human Rights Commissions, International and National Equality Laws uphold equality and prohibit all employers, service providers and providers of education, from discriminating against, harassing or victimising individuals with on basis of personal characteristics.
recognizes the fact that the social identifiers such as race, gender, socioeconomic status, personal characteristics, etc. lead to discrimination and unequal treatment. Equity relates to the belief that all individuals need to be provided an equitable environment and access to equal opportunity.
Equality refers to uniform and even distribution of resources among all irrespective of individual differences. Treating everyone equally does not promote equality; it can perpetuate hierarchies and raise barriers, impediments and gaps encountered by certain category of individuals. Equity considers the specific needs of disadvantaged individuals and entails distribution of resources and access to opportunities in a manner that would help them to overcome handicaps. Thus, in an equitable environment, an individual or a group would be given what is required to give them equal advantage. It could be more or different than what the general population receives. Equity is an ideal and a moral imperative. It aims to level the playing field with appropriate resources and opportunities so that all get a chance to succeed.
is a process of bringing together individuals who are traditionally excluded in organization as equal and active members of the community. It entails creating an environment wherein individuals, irrespective of their identity, are welcomed, valued, respected, given equal opportunities for full participation. Inclusion must operate at all levels, providing equitable access to resources, representation on decision-making forums and leadership positions. An inclusive workplace endeavors to remove discrimination, generates a sense of belonging and personal value with transformative impact on organizational culture.
is a concept that an individual’s identity has many aspects, all of which are interconnected. Various dimensions include age, race, sex, gender, sexual orientation, ability/disability, ethnicity, class, caste, religion, socioeconomic status, regional and linguistic identity, etc. These interconnected attributes manifest in an individual as multiple identities. Individuals experience themselves and the world through different lenses. Similarly different identities affect the way individuals are viewed in society. Societal perceptions strongly influence an individual’s lived experience and sense of belonging. Understanding intersectionality is an important component of actions for enhancing equity, diversity and inclusion.